These calculations are important as they provide data that is necessary in determining the cost of treatment and the efficiency of the process control equipment. The accuracy of the flowmeters and pumping capacities can be checked and the measurement of flows, contributed by various sources, such as ground water run-off or industrial wastes, can be estimated with some degree of accuracy. Rates of flow must be determined for proper sizing of clarifiers, aeration tanks, grit chambers, filters, feed rate calculations, etc.
Example 1
A channel 2 m wide has a water flowing to a depth of 0.5 m. What is the daily FLOW in the channel if the velocity of the water is 0.75 m/s?
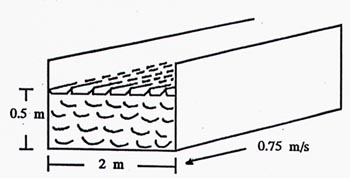
Rate of flow = width X depth X velocity
= (2 m) X (0.5 m) X (0.75 m/s)
= 0.75 m3/s
However, we are asked to find the daily flow.
Daily flow = rate of flow X 60 s/min X 1440 min/d
= (0.75 m3/s) X (60 s/min) X (1440 min/d)
= 64 800 m3/d
Example 2
What is the daily FLOW in a 300 mm diameter pipe that is flowing 75% full if the velocity is 40 m/min?

1. Convert applicable data to the same units:
Diameter = 300 mm =0.3 m
Radius = diameter/2 = 0.15 m
2. Apply data to formula:
Rate of flow = cross sectional area X velocity
=
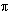 r2 X v
r2 X vHowever, the pipe flows at 75% full.
Rate of flow = 0.75 (pi r2 X v)
= 0.75 X (3.14) X (0.15 m) X (0.15 m) X (40 m/min)
= 2.1 m3/min
We need to convert 2.1 m3/min to a standard expression of flow rate. Either L/s or m3/d are correct and we are asked to put the answer in terms of daily flow (m3/d).
Daily flow = volume of flow X 60 min/h X 24 h/d
=(2.1 m3/min) X (1440 min/d)
=3024 m3/d