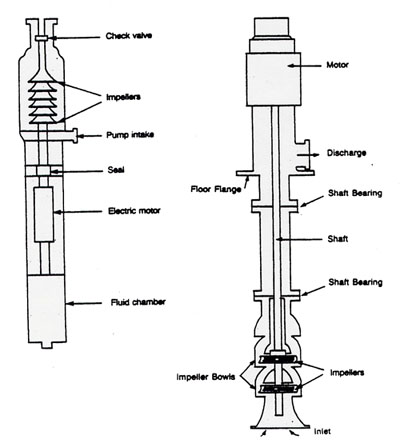
In the turbine pump, the impeller is surrounded by diffuser vanes which provide gradually enlarging passages in which the velocity of the water leaving the impeller is gradually reduced. This increases the pressure being applied to the water.
The turbine-type pump is used where greater lifting action is required, as in water wells.
Here are diagrams of typical turbine pumps.
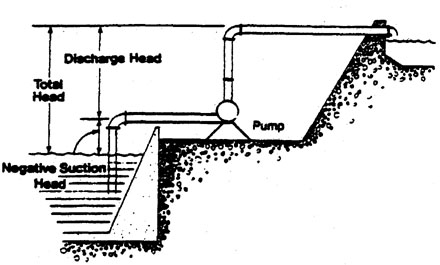 The actual discharge head in a given system will depend on a number of factors, like the speed of the pump, and the design of the impeller and the pump.
The actual discharge head in a given system will depend on a number of factors, like the speed of the pump, and the design of the impeller and the pump.
Note too that we have indicated that the suction head in this diagram is a “negative” suction head.
- When the water level is below the center of the impeller, as it is in this diagram, it is called a negative suction head. The maximum practical negative suction head is about 5 metres (16 feet) at sea level.
- When the water level is above the impeller center, it is called a positive suction head.
A pump will operate more efficiently when the negative suction head is less than 5 metres (16 feet). Efficiency will decrease as this lift increases. Permanent pumping installations are normally designed to accommodate these conditions.